Running an enterprise-grade secrets management platform yourself is not easy. These systems need to be highly available, secure, and resilient across regions — this requires deep expertise and significant ongoing investment. For many organizations, building and maintaining disaster-recovery-ready secrets management infrastructure on their own introduces unnecessary complexity, cost, and operational risk without delivering much differentiation.
The challenge for cybersecurity teams is finding a SaaS secrets management solution that has proven itself as a secure, reliable option. One solution worth testing is HCP Vault Dedicated, which delivers Vault Enterprise (the self-managed version of HashiCorp Vault) as a fully managed, single-tenant service. HCP Vault includes:
- High availability
- Automated cross-region disaster recovery
- Data-plane isolation
To dive deeper into how teams can offload operations, scaling, and recovery for their Vault security and secrets management platform, we created a guide to help you assess your security operations and security platform disaster recovery architecture.
HCP Vault Dedicated SecOps features
HCP Vault Dedicated removes the need for your operations team to run Vault and provide the high levels of uptime that you need if you want to maintain secure access for your applications and infrastructure. At large enterprises, this can involve hundreds of thousands secret requests every hour. With the SaaS version of Vault Enterprise, you get:
Built-in high availability
Every production HCP Vault Dedicated cluster runs as a three-node, highly available (HA) deployment, monitored and maintained by HashiCorp SREs. If a node becomes unhealthy, HCP handles replacement automatically, helping ensure continuity without internal teams managing cluster lifecycle.
Cross-region disaster recovery made simple
Instead of engineering multi-region replication and failover logic yourself, HCP Vault Dedicated bakes it into the platform:
- Configure a backup HashiCorp Virtual Network (HVN) in any supported region
- If the primary region experiences an outage, HCP automatically fails over the cluster to the backup region
- Vault’s DNS address remains the same, minimizing client disruption
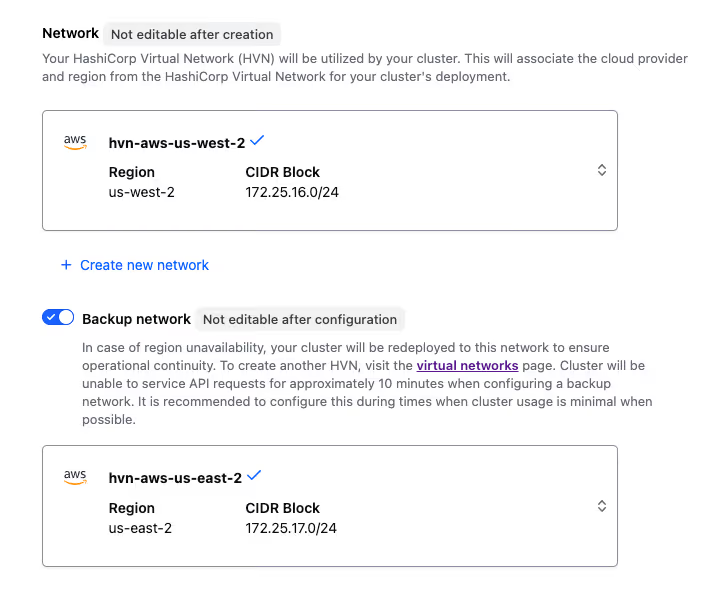
This offers enterprise-grade disaster recovery with dramatically reduced operational overhead.
Resilience even during control plane outages
HCP uses a separate control plane and data plane. Even if the HashiCorp Cloud Platform (HCP) portal or API is disrupted, your dedicated Vault cluster continues to operate, and DR failover can still occur if preconfigured.
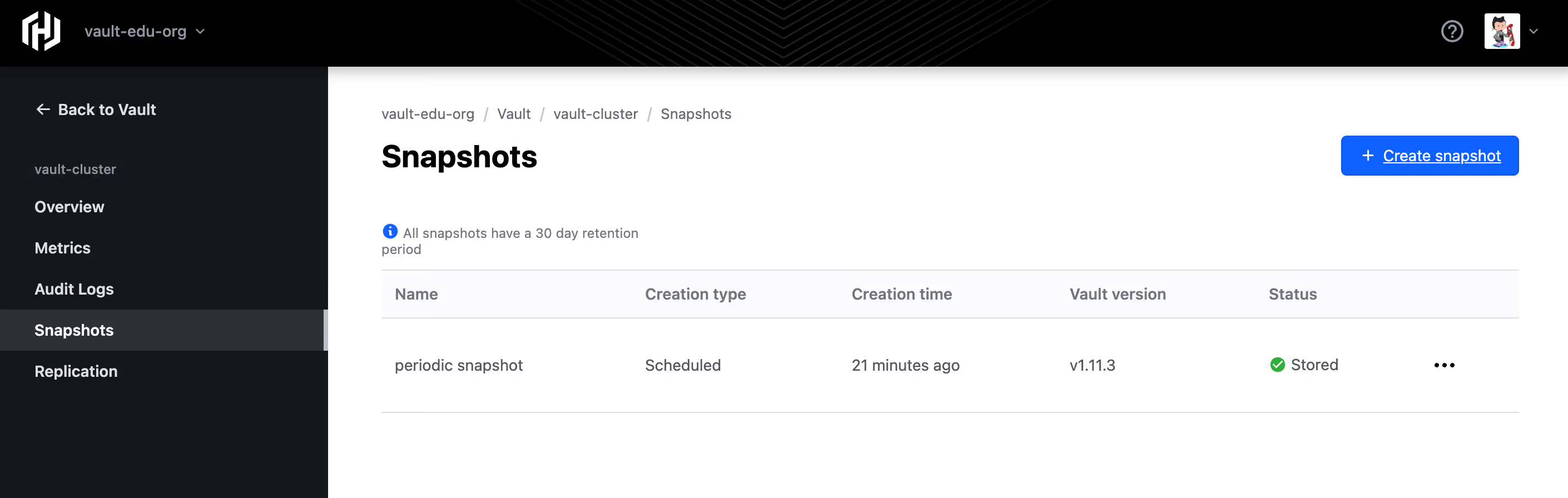
Managed snapshots and restore
Backups of your Vault cluster state (called snapshots) are automatically retained (depending on your tier), enabling cluster restoration even after accidental deletion or corruption — no custom backup pipeline required.
HCP Vault: Do more with fewer resources
1. Bridges skills gaps for secret management operations
Running Vault reliably as an enterprise secrets management platform requires expertise in distributed systems, security hardening, replication, and DR planning.
2. Reduces infrastructure and operational costs
Avoid the overhead of:
- Architecting multi-region failover
- Operating HA clusters
- Managing upgrades, patches, and security hardening
- Running 24/7 monitoring
- Troubleshooting outages
HCP manages these tasks so your teams don’t have to.
3. Frees teams to focus on differentiation
- Operators and developers should be focused on building and managing new features or applications that bring value to customers. Managing Vault SRE tasks in-house doesn’t add to your business value, and it doesn’t differentiate you from your competitors in a meaningful way.
4. Simplifies hybrid and multi-cloud adoption
HCP Vault Dedicated integrates across hybrid and multi-cloud environments via HVN peering, transit gateway, or PrivateLink, functioning as a secure managed data-plane deployment connected directly into your environment.
5. Ensures consistent enterprise-grade security
HCP applies hardened defaults, operational best practices, and automated monitoring, delivering security standards that traditionally require large internal teams.
Disaster recovery architecture checklist for HCP Vault Dedicated
This checklist is designed to help CIOs, CISOs, and other cybersecurity decision-makers assess their disaster recovery architecture for HCP Vault secrets management.
Deployment and tiering
- Select Essentials or Standard tier to enable cross-region DR
- Plan for multi-region footprint early in the deployment lifecycle
Network architecture
- Create a backup HVN in a different region with a non-overlapping CIDR
- Ensure network connectivity (peering, transit gateway, or VPN) to both primary and backup HVNs
- Confirm firewall rules allow traffic to load-balancer IPs in both regions
Connectivity and client behavior
- Verify clients can resolve and reach Vault post-failover (DNS stays consistent)
- If using the HCP proxy address, be aware it will not route traffic when the cluster is active in the backup region
Operational considerations
- Expect less than 10 minutes of unavailability when enabling backup networks on an existing cluster
- Subscribe to failover and recovery notifications
- Validate that logs and metrics properly reflect DR-prefixed cluster IDs after failover
Backup and restore
- Understand snapshot retention policies (e.g. 30 days for certain tiers)
- Create a restore runbook including restoring to alternate regions if necessary
Testing and governance
- Perform periodic DR simulations to validate application continuity
- Document responsibilities during failover and failback
- Update compliance frameworks with DR logging and audit behaviors
The outcomes of SaaS for secrets management
HCP Vault Dedicated combines Vault Enterprise’s proven DR capabilities with the convenience and efficiency of a managed service for your organization's secrets management. With built-in HA, automated cross-region failover, snapshot management, and data-plane isolation, organizations gain world-class resilience — without needing to build and maintain world-class infrastructure.
The result:
- Lower operational overhead
- Stronger security posture
- Faster innovation
- A more efficient team that can do more with fewer resources
Let your teams test drive HCP Vault Dedicated for free, and get in touch if you’d like to talk about your secrets management practices.
FAQs
What happens to Vault clients during a regional outage?
HCP Vault Dedicated is designed so applications using Vault as their secrets manager experience minimal disruption during a regional outage. When cross-region disaster recovery is enabled, HCP automatically fails over the Vault cluster to a preconfigured backup region while preserving the same DNS address. This allows applications to continue retrieving secrets and encryption keys without client-side reconfiguration.
How long does disaster recovery failover take?
Failover to a backup region typically completes within minutes once an outage is detected. Because disaster recovery is built directly into the managed HCP Vault Dedicated service, teams do not need to manually promote clusters or coordinate complex recovery workflows during an incident.
Can Vault continue operating if the HCP control plane is unavailable?
Yes. HCP Vault Dedicated uses a separate control plane and data plane. Even if the HCP portal or API is unavailable, the Vault data plane continues operating, and secrets management workflows — including authentication and secret retrieval — remain functional. Preconfigured disaster recovery can still occur without control plane access.
from HashiCorp Blog https://ift.tt/MkYCtJX
via IFTTT