What’s new in Windows Server 2022
The latest release of Microsoft’s server operating system, Windows Server 2022, was released in August 2021. It comes with several new features and improvements, including:
- Security. Secured-core server, SMB over QUIC, and enhanced Windows Defender.
- Integration with Azure. Multiple hybrid options for seamless integration with Azure (Azure Arc-enabled servers, Azure File Sync, Azure Automanage, and Azure Stack HCI).
- Container Support. Improved container support includes containerization of server roles and support for Kubernetes.
- Storage Spaces Direct. New Storage Spaces Direct capabilities include enhanced resiliency, deduplication, and compression.
- Performance. Faster startup time, improved performance for Storage Spaces Direct, and improved network performance.
- Windows Admin Center. New dashboard, tools, and improved performance.
Overall, Windows Server 2022 is a major update that provides several new features and enhancements, making it a powerful platform for modern workloads and hybrid environments.
Disclaimer
In fact, most of our posts address technical issues. Licensing, in its turn, is a legal matter. I am not a lawyer and I have not consulted with a lawyer on the issues covered in this post either. Here, I intend to discuss the concepts of a specific licensing detail. Please note that the post neither gives legal advice nor interprets the policy. Neither I nor Altaro software are authorized for legal consulting, thereby, do not view the post as such. This implies that none of us can be held responsible for any negative outcomes related to the usage of any of our post’s contents, including the cases when it is thought to be an error on our part or a misunderstanding on yours. If any questions arise, please, take your time and get official answers to avoid being fined for policy violation. For any inquiries, contact Microsoft directly, or your reseller. Authorized resellers have employees authorized to answer licensing questions. You can also check the Product Use Rights document, the most transparent material published by Microsoft on the subject so far.
OEM Licenses
The main difference between OEM and Volume Licenses is that the former are not transferable. This post overviews Volume Licenses, an agreement that users make with Microsoft through resellers. OEM licenses, in their turn, can be customized by any equipment manufacturer, thus, rules may vary. Regarding this fact, do not expect an OEM license to work in the same way as a Standard Volume one.
Microsoft Windows Server Products
Apart from licensing policies, Microsoft has changed their product line. Windows Server 2022 is available in three main editions:
- Essentials is an ideal solution for small businesses comprising up to 25 users and 50 devices;
- Standard suits perfectly for physical systems with insignificant virtualization;
- Datacenter is designed for cloud-based environments and systems with a high virtualization level.
Hyper-V Server 2019 is a free edition of the Windows Server 2019 operating system that only includes the Hyper-V role. It enables hosting multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. However, it’s not a part of the 2022 release.
There are also another edition available:
- MultiPoint Premium Server enables the multiple users accessing one PC. Bear in mind that there is only academic license available;
Now, let’s shed light on the licenses for small businesses. Essentials licensing provides access for up to 25 users and 50 devices. Importantly, the license does not require client’s access. Foundation exclusion does not remarkably impact users since the option was available only on the OEM channel. End-users got it supplied only with a ready server. Essentials, in its turn, could be purchased in terms of corporate licensing and used with the already available hardware.
The Rule for Windows Server Licensing
Users are charged for each physical processor’s core, instead of the entire physical processor. For instance, you could purchase a single license for a 16-core processor before instead of buying multiple licenses for several processors with fewer cores.
Every core needs to be licensed separately. This approach towards licensing seems clear if the modern trends in processor manufacturing are considered. Compute power is enlarged rather intensively (by using multicore processors) than extensively (by employing multiple physical sockets).
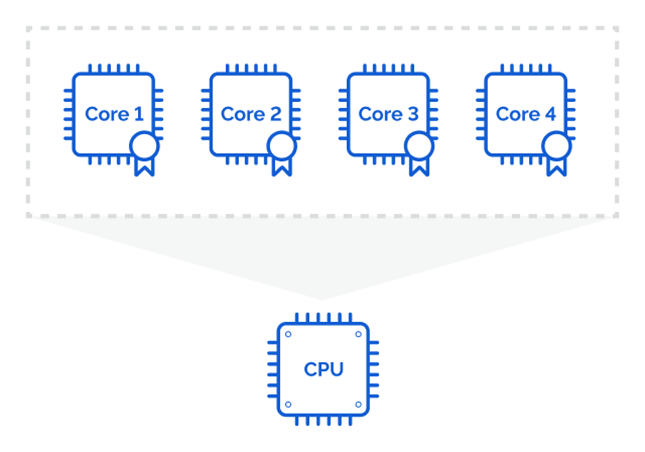 The license for processors comprises at least 8 licensed units, while the one for servers includes over 16 units. The image below describes how Windows Server per-core licensing works (from 2016 and onwards).
The license for processors comprises at least 8 licensed units, while the one for servers includes over 16 units. The image below describes how Windows Server per-core licensing works (from 2016 and onwards).
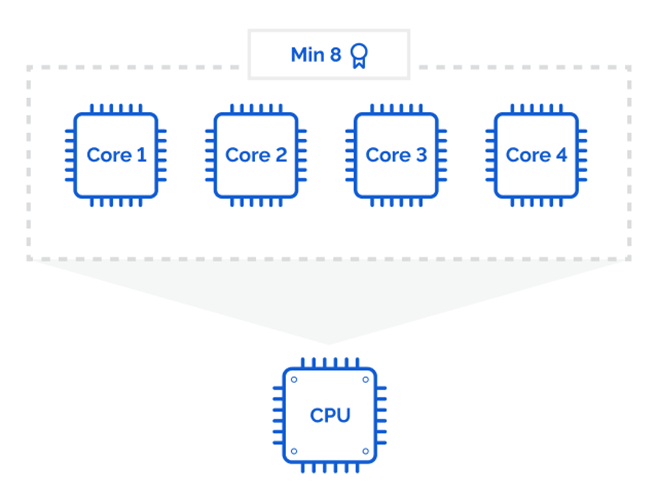
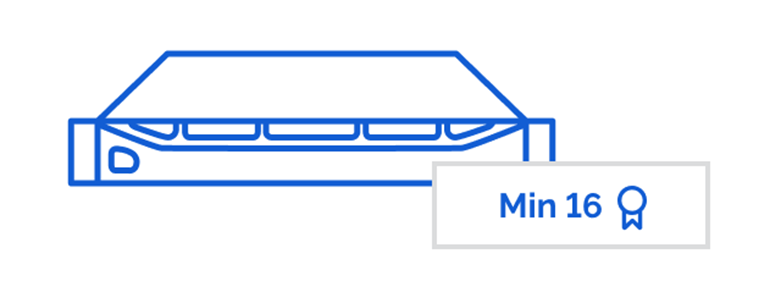 Each couple of cores is licensed. Organizations must purchase a minimum of 16 core licenses per server (additional licenses required for each set of 2 cores). For example, a server with 24 cores would require 12 additional core licenses. Each core license allows for the installation of Windows Server on a single physical or virtual core.
Each couple of cores is licensed. Organizations must purchase a minimum of 16 core licenses per server (additional licenses required for each set of 2 cores). For example, a server with 24 cores would require 12 additional core licenses. Each core license allows for the installation of Windows Server on a single physical or virtual core.
| Server licensing | 1-processor server | 2-processor server | 4-processor server | |||
| Windows Server Standard & Datacenter | Required # cores Licenses | Required # 2-pack SKUs | Required # cores licenses | Required # 2-pack SKUs | Required # cores licenses | Required # 2-pack SKUs |
| 2 cores per processor | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 |
| 4 cores per processor | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 |
| 6 cores per processor | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 |
| 8 cores per processor | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 |
| 10 cores per processor | 16 | 8 | 20 | 10 | 40 | 20 |
Important: Core licenses usually come in 2-packs or 16-packs (optional). Eight 2-packs and one 16-pack are essentially the same in price and use rights.
The Hyper-V Server License
Virtualization licensing policies remain unchanged. The Standard license enables two VMs deployed having the host system occupied entirely by their servicing. For more virtual machines deployment, users need additional licensing of all their processors’ cores regarding the current policies.
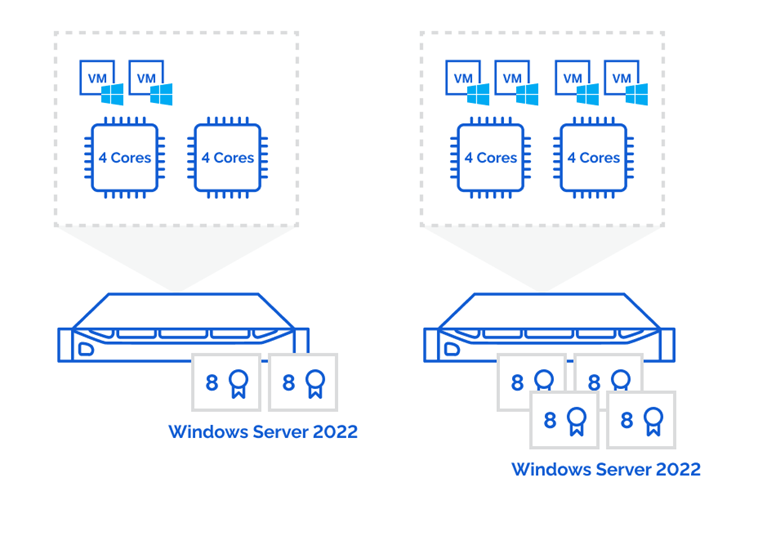 The Datacenter edition is an immensely powerful option, but a costly one. Running it for personal operations is like using a sledgehammer to crack a nut. Practically, there is no particular reason to choose this licensing unless you’re intending to run more than 10 VMs.
The Datacenter edition is an immensely powerful option, but a costly one. Running it for personal operations is like using a sledgehammer to crack a nut. Practically, there is no particular reason to choose this licensing unless you’re intending to run more than 10 VMs.
Conclusion
This article covers the most significant aspects of Microsoft Windows Server 2022 licensing. The OS is available in two editions: Standard and Datacenter. Windows Server per-core licensing requires organizations to purchase licenses based on the number of physical processor cores in the server. This model was introduced with Windows Server 2016 and has continued with subsequent versions, including Windows Server 2022. Such licensing policy affects only users with powerful multicore processors (one paired license costs 1/8 of the Windows Server 2012 license). Virtualization policies remain unchanged.
More Questions
I usually am happy to discuss some issues with you. However, we’re not going to be that open in this particular case. I am not authorized to provide legal advice since I do not want anyone who reads this to get in trouble. The only purpose of this post is to clear up the initial confusion that many people have on the subject. If I haven’t explained it clear enough, talk to a licensing expert. Run it through your legal department. Licensing is a confusing topic and not worth making mistakes on. Get an expert on the phone, explain what you have and what you want to accomplish, and you’ll have a legitimate answer shortly.
This material has been prepared in collaboration with Alex Khorolets, StarWind Solutions Engineer, and Viktor Kushnir, Technical Writer with almost 4 years of experience at StarWind.
Related materials:
from StarWind Blog https://bit.ly/3Nmic6e
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment