Access to today’s IT environments must be kept secure. In order to ensure secure and efficient access to corporate resources the best is to use products that secure those accesses for you. With the rise of remote work and the proliferation of mobile devices, the need for a robust and comprehensive solution for remote access management is more critical than ever.
VMware has a product that is built just for that and its name is VMware Unified Access Gateway (UAG). The product offers a secure, scalable, and user-friendly platform for managing remote access. In this blog post, we will show some details about the security, deployment steps. It’s no mean to be a detailed -step-by-step process, just an overall product details of VMware UAG from an admin’s perspective.

What’s new in the latest release of VMware UAG
- The latest release has added compatibility with Horizon Connection Server’s support for setting enforcement state from clients with the same or a higher certificate checking mode.
- Support for enforcing virtual channel restrictions with Blast protocol. This list overrides any settings applied through the Horizon Agent.
- Improved compatibility with Web Reverse Proxying to web services using NTLM authentication.
- Enhancements in SAML authentication for the Admin UI administrator login.
- New support for Tunnel Edge Service.
- Updates to the underlying PhotonOS Linux packages versions and Java components version.
Importance of Security in Remote Access
Before we dive into VMware UAG’s features and deployment, let’s underscore the critical importance of security in remote access solutions. In today’s interconnected world, where sensitive corporate data is accessed from various devices and locations, maintaining the highest level of security is non-negotiable. Here are some reasons why security is paramount in remote access solutions:
- Data Protection – Remote access solutions deal with sensitive data, intellectual property, and confidential information. A breach could lead to data leaks, financial losses, and reputation damage.
- Compliance – Many industries have strict compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) that mandate data protection measures. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in legal penalties.
- Cyber Threats – The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving. Attackers are constantly devising new tactics to infiltrate networks and steal data. A robust security framework is necessary to defend against these threats.
- User Authentication – Ensuring that only authorized users gain access to corporate resources is a fundamental aspect of security. Strong authentication mechanisms are crucial.
- Endpoint Security – As users access corporate resources from various devices, ensuring the security of these endpoints is vital. Malware-infected devices can become entry points for attackers.
VMware Unified Access Gateway (UAG) – An Overview
VMware Unified Access Gateway is a critical component of VMware’s Digital Workspace platform. It is designed to provide secure remote access to corporate resources for a wide range of devices, including PCs, Macs, smartphones, and tablets.
Unified Access Gateway is a VMware hardened Linux based virtual security appliance designed to protect remote user access to end-user computing resources such as virtual desktops and applications. It is designed to operate with the following VMware solutions:
- Desktop and App Virtualization with Horizon 7/8 and Horizon Cloud
- Workspace ONE Access
- Workspace ONE UEM
- Per-App Tunnel
- Content Gateway
- Secure Email Gateway
Screenshot from VMware.
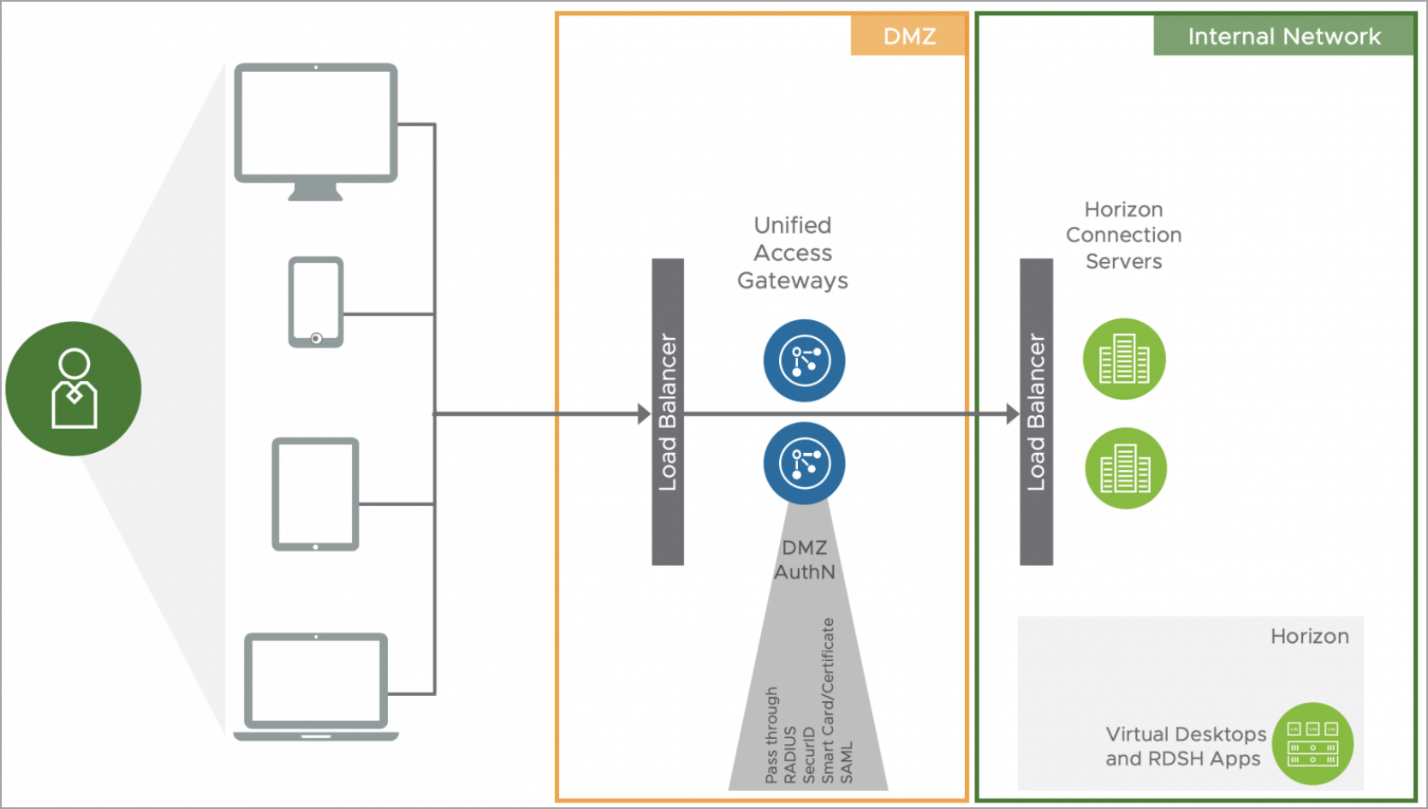
UAG offers several key features that make it an attractive choice for organizations looking to bolster their remote access capabilities:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): UAG enables users to access multiple applications and resources with a single set of credentials. This enhances user experience while maintaining security.
- Per-App Tunneling: UAG allows organizations to control access to specific applications, rather than providing unfettered access to the entire network. This helps in limiting potential attack vectors.
- Device Compliance Checking: Administrators can enforce policies to ensure that only compliant and secure devices can access corporate resources.
- Load Balancing and High Availability: UAG supports load balancing for high traffic environments and offers high availability options to ensure uninterrupted access.
Deployment Steps
Unified Access Gateway distributed as a single file (OVF) that is pre-hardened and tested overall by VMware. All configuration settings can be pushed during deployment so that Unified Access Gateway is “production-ready on first boot” and using automated deployment, and take less than 2 minutes. There is no need to separately configure or harden the appliance after it is deployed.
Depending on the architecture you’re targeting, you can deploy it within vSphere or ESXi environments, Amazon AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure, Hyper-V or Google Compute Engine (GCE).
Deploying VMware Unified Access Gateway can be a complex task, but VMware has provided comprehensive documentation and resources to guide administrators through the process. Here is an overview of the deployment steps:
1. Prerequisites:
- Ensure that you have a VMware vSphere environment set up.
- UAG needs DNS configuration for the appliance, and netmask, default gateway, and subnet to be defined, for each network that is enabled during deployment.
- Get the UAG OVA (Open Virtualization Appliance) file from VMware’s official website.
2. Installation and Configuration:
- Deploy the UAG appliance using the OVA file in your vSphere environment.
- Configure the network settings, including IP address, subnet mask, and DNS settings.
- Access the UAG configuration interface through a web browser and perform the initial setup.
Note: There is a great tool that is available as a VMware Fling called the Unified Access Gateway Appliance Installer. You can check out the details here:
Screenshot from the test deployment via the VMware Fling
3. Authentication Configuration:
- Integrate UAG with your organization’s identity provider (e.g., Active Directory, LDAP, or RADIUS) for user authentication.
- Configure Single Sign-On (SSO) to streamline the login process.
4. Application Configuration:
- Define the applications and resources that users will access through UAG.
- Configure per-app tunneling rules to control access to specific resources.
5. Security Configuration:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security.
- Set up endpoint compliance checks to ensure device security.
6. Load Balancing and High Availability:
- Implement load balancing if your environment requires it.
- Set up high availability to ensure continuous access in case of appliance failures.
7. Testing and Monitoring:
- Thoroughly test the remote access functionality to ensure it meets your organization’s requirements.
- Implement monitoring and alerting to proactively identify and address issues.
8. Documentation and Training:
- Document the configuration and deployment for future reference.
- Train administrators and end-users on how to use UAG effectively and securely.
System Requirements
From an administrator’s perspective, understanding the system requirements for deploying VMware UAG is crucial to ensure a smooth and efficient deployment. Here are the key system requirements:
1. VMware vSphere:
- VMware UAG is designed to run within a vSphere environment. Ensure that your vSphere infrastructure is properly configured and meets the minimum version requirements.
2. Virtual Hardware:
- UAG requires a minimum of 2 vCPUs and 4 GB of RAM for basic functionality. However, requirements may vary based on your organization’s specific needs.
3. Identity Provider:
- Prepare your organization’s identity provider, such as Active Directory or LDAP, for integration with UAG for user authentication.
4. Certificates:
- Obtain SSL certificates for securing communication between UAG and client devices. Ensure that the certificates are valid and properly configured.
5. Application and Resource Configuration:
- Identify the applications and resources that will be accessed through UAG and gather the necessary configuration details.
Final Words
VMware Unified Access Gateway is a very robust and flexible solution to protect access for VMware Horizon, Workspace ONE and desktop environments over public networks.
In the era of remote work and heightened security concerns, VMware Unified Access Gateway stands out as a robust solution for managing secure remote access to corporate resources.
As an administrator, understanding the importance of security, deployment steps, and system requirements is essential to successfully implement this solution in your organization. VMware UAG’s features, including single sign-on, per-app tunneling, multi-factor authentication, and device compliance checking, offer a comprehensive approach to remote access management that prioritizes both security and user experience. By following the deployment steps and meeting the system requirements, you can ensure that your organization benefits from secure and seamless access to critical resources, regardless of where your users are located. We do hope that the Fling we tested will be integrated into the VMware UAG in the future releases as it greatly eases the installation process.
from StarWind Blog https://bit.ly/3O9CL5G
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment