The Good | DoJ Indicts Crypto Mixer Operators & Deletes PlugX Malware from Over 4000 Machines
The DoJ has indicted three Russian nationals – Roman Vitalyevich Ostapenko, Alexander Evgenievich Oleynik, and Anton Vyachlavovich Tarasov – for operating cryptocurrency mixing services Blender[.]io and Sinbad[.]io. These mixers, used heavily by ransomware gangs and North Korean hackers, laundered criminal proceeds, including ransomware payouts and stolen cryptocurrency. Blender[.]io operated from 2018 to 2022 and helped Lazarus Group launder $500 million of the $617 million stolen in the Axie Infinity Ronin bridge attack. After the site was shut down, Sinbad[.]io emerged, offering similar services until it was seized in November 2023 in a joint law enforcement operation.
A joint statement from the U.S., South Korea, and Japan came just days after the indictment, revealing that North Korean threat actors have stolen over $659 million in cryptocurrency. Crypto mixers are a significant part of how actors profit from crypto-heists and remain a significant threat to the integrity of the global financial system.
A court-ordered FBI operation has successfully removed PlugX malware from over 4,200 infected computers across the U.S. PlugX has long been a thorn in the side of governments, businesses, dissidents, and NGOs worldwide. First observed in 2008, the remote access trojan (RAT) is primarily used by PRC-sponsored hacking outfits and enables attackers to steal sensitive information, remotely control infected devices, and spread to additional systems via USB drives.
The FBI and DOJ announced a court-authorized operation that removed PlugX malware from thousands of computers in the U.S. and abroad. PRC-sponsored hackers used PlugX to target businesses, governments, and Chinese dissidents. Find more information here: https://t.co/4facCNfk5P pic.twitter.com/j7kPCHeu1x
— FBI (@FBI) January 14, 2025
The operation kicked off in July 2024 and involved an international effort between law enforcement and cybersecurity partners who managed to sinkhole a PlugX variant’s server and issue a self-delete command to erase the malware, registry keys, and directories from infected machines without affecting legitimate system functions.
The Bad | New Evidence Connects DPRK’s IT Worker Fraud to 2016 Crowdfunding Scam
Infrastructure links between the DPRK’s fraudulent IT worker schemes and a crowdfunding scam from 2016 have emerged, shining a light on the extent of North Korea’s early experimentation with illicit money-making tactics.
Exposed in 2023, North Korea’s ongoing fraudulent IT worker scheme involves DPRK actors using fake identities to secure jobs globally, generating revenue for the sanctions-laden regime. These workers have often been tied to the 313th General Bureau under North Korea’s Workers’ Party and subsequently deployed to China and Russia to work for front companies like Yanbian Silverstar and Volasys Silver Star, both sanctioned by the U.S. in 2018 for facilitating North Korean labor exports.
In a new report, researchers examined the 17 domains seized by U.S. authorities back in October 2023, all impersonating IT service companies to mask North Korean workers’ identities as they applied for freelance jobs. One domain, silverstarchina[.]com, was traced to Yanbian Silverstar offices located in the Yanbian prefecture. The same street address and email were reused to register other domain names.
This included kratosmemory[.]com, a domain used in a 2016 IndieGoGo crowdfunding campaign, which managed to raise $21,877 but was exposed as a scam when backers received no products or refunds. Researchers found that the WHOIS registrant information for kratosmemory[.]com was last updated in mid-2016 to a persona called ‘Dan Moulding’ – a match to the IndieGoGo user profile used in the Kratos scam.
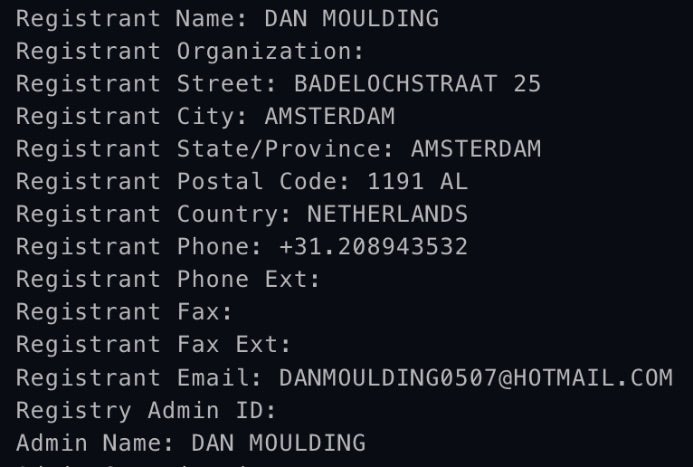
Though the 2016 scam is considered low complexity compared to the DPRK’s current IT worker schemes, it shows an early example of North Korea’s efforts to generate revenue while evading sanctions, demonstrating the regime’s willingness to evolve and diversify its financial tactics.
The Ugly | GRU-Linked APT Conducts Cyber Espionage on Kazakhstani Diplomatic Relations
UAC-0063, a threat actor likely associated with GRU-backed APT28, has been targeting Kazakhstan and neighboring countries with multi-stage infections to enable continuous data extraction in ongoing cyberespionage campaigns.
CERT-UA first exposed UAC-0063 in April 2023, revealing its attacks on government entities that reach across Ukraine, Israel, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. Now, new analysis from researchers explains how UAC-0063 now leverages spearphishing emails that contain malicious Microsoft Office documents from Kazakhstan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs. These documents, like intergovernmental letters and administrative notes, trigger an infection chain called “Double-Tap”, which drops the HATVIBE malware.

HATVIBE is a Visual Basic Script (VBS) backdoor that operates as a loader for additional modules, paving the way for Python-based CHERRYSPY backdoor. CHERRYSPY allows the attackers to execute code received from a C2 server. Researchers note that the original source of the documents are unknown but were likely exfiltrated in a previous attack.
UAC-0063’s focus on targeting diplomatic sectors is a reflection of Russia’s cyberespionage efforts in Kazakhstan. Since the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Kazakhstan has balanced support for Ukraine’s territorial integrity. This stance, coupled with efforts to strengthen ties with Western powers, China, and its neighboring Central Asian states, has increased Kazakhstan’s strategic significance in the political sphere. Kazakhstan’s steady departure from Russia’s influence also explains the espionage campaign’s emphasis on weaponized documents related to Kazakhstan’s foreign relations.
These campaigns continue the GRU’s efforts in gathering intelligence on Kazakhstan’s geopolitical alliances, trade routes, and strategic projects to counter competing powers and maintain Russia’s influence in Central Asia.
from SentinelOne https://ift.tt/xLvUosz
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment